People often talk about the many environmental benefits of solar energy for good reason: Solar is one of the easiest and most effective ways for people and companies to think globally and act locally and have a direct bearing on the health of our planet and its inhabitants.
But how exactly does solar help the environment? We explain below, and also explain how these environmental benefits are inextricably linked to human health.
The Environment/Health Link
Global warming and climate change are associated with the planet’s health, but we should not forget that climate change also has a direct impact on our health. All who inhabit planet Earth—including human beings, other animals and even plant species—are affected by the health of the planet.
Since solar energy is good for the environment, it’s also good for human health.
The Chain of Events
It all starts when you choose to rely on the sun instead of fossil fuels to produce electricity. This flow chart conveys the impacts of that decision. We explain each item in detail below.
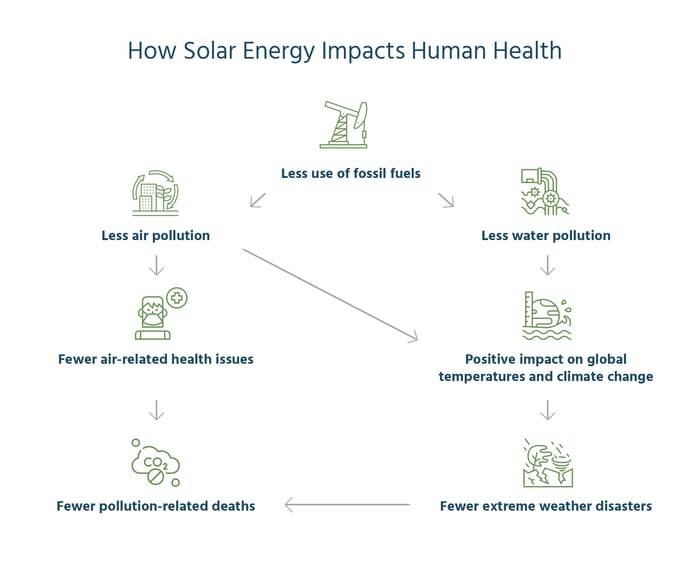
Less Use of Fossil Fuels
Most electricity is produced by burning fossil fuels like natural gas, oil and coal. Natural gas is increasingly obtained through the controversial method called hydraulic fracturing, also known as fracking. Nuclear power is another traditional fuel “source”.
The process of extracting fossil fuels from the Earth and burning those fuels to make electricity is well-known to be harmful to the environment (and expensive).
When you replace fossil-fueled electricity with solar-powered electricity, you reduce the use of fossil fuels and their harmful side effects. This decision also provides you with some independence from your utility and their shareholder-driven decisions. And greater use of renewable energy sources like solar provides the U.S. with greater energy independence and less reliance on global fossil fuel sources like oil from the Middle East.
Solar’s Impact on Air Pollution
The process of burning fossil fuels produces gases that are harmful to the planet and to people. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the main greenhouse gas produced during power production, although other toxic gases are also created as this graph from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) shows.
These gases are considered “greenhouse gases” because they contribute to changes in the Earth’s atmosphere that cause a greenhouse-like effect and cause the planet’s temperature to rise. As the Earth gets warmer, ecosystems are disrupted, species face extinction, extreme weather events become more common and health risks to human beings escalate.
The process of making electricity from solar, on the other hand, produces no air pollution, as the EIA confirms.
Solar’s Impact on Water Pollution
Many fossil fuel plants require a lot of water in the power generation process. Fossil fuels are burned to heat water, creating steam that spins turbines to generate electricity. Coal plants often pump the water they use back into the originating body of water at a much high temperature, which adversely affects the marine ecosystem.
Solar, on the other hand, does not deplete or pollute water supplies, although some water is used in the manufacturing of the photovoltaic (PV) cells, just as some water is used in most manufacturing processes. In addition, some larger solar power plants may use water for panel cleaning.
(Solar thermal systems are different from solar PV systems, and use more water.)
Energy Production’s Impact on Extreme Weather
The pollution from fossil-fueled power plants is a major factor in global warming and climate change. Numerous extreme weather events are likely linked to climate change: 
- More frequent, longer and intense heat waves
- More frequent and longer droughts
- More frequent wildfires that burn longer and across a wider area
- More flooding caused by rising sea levels
- More frequent and intense hurricanes
People sometimes question how the world can be experiencing more snowy weather in the midst of climate change. Here’s how Earth Justice explains the phenomenon: Warmer temperatures increase evaporation, which puts more water vapor in the atmosphere, which creates more rain and snow. Areas with heavy precipitation are getting wetter while traditionally dry areas are getting drier.
Energy Production’s Impact on Human Health
The human health impacts of burning fossil fuels for energy are, to be blunt, frightening. The burning of fossil fuels “releases pollutants that lead to early death, heart attacks, respiratory disorders, stroke, exacerbation of asthma, and…may even be related to autism spectrum disorder and Alzheimer’s disease,” according to the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Climate Nexus lists the following findings based on research from experts at institutions including MIT, ScienceAdvances and the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics:
- 52,000 premature deaths a year are caused by air pollution created during the fossil fueled power generation process
- Nearly $5 billion in health costs related to premature births stems from fossil fuel emissions
- Women in Pennsylvania who live within two miles of a fracking site are more likely to have low-weight babies, according to a long-term study
- People who work in mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction are almost four times as likely to suffer a severe or fatal injury than the average U.S. worker
Solar, on the other hand, can reduce these pollution-related health issues, which in turn could lower overall healthcare costs—always a good thing!
It stands to reason that the more we rely on solar energy to replace fossil fuels, the better off we’ll all be. And there is plenty of sunlight to go around. An oft-quoted statistic says enough sun hits the Earth in an hour to power the planet for an entire year.
Does Solar Have Negative Environmental Impacts?
There are a few relatively minor concerns about solar’s environmental impact.
As the EIA states, “some toxic materials and chemicals are used to make the photovoltaic (PV) cells that convert sunlight into electricity”. But the impact is negligible compared to fossil fuels.
With the solar industry still relatively young, the impact of disposing of panels that are no longer producing remains to be determined. But the industry is already working toward recycling and safe disposal practices. And, with many panels expected to last beyond their 25-year warranties, it will be some time before any large-scale disposal of panels is needed.
If you worry about trees being cut to make room for solar, here’s some guidance from the Sierra Club. In general, removing some trees to install a home or small commercial solar energy system is a beneficial trade-off for the environment. Clear-cutting acres of forest for a massive solar power plant is a more complicated story.
Side Benefits
Back to the positives, in addition to lower electric bills and all these health and environmental benefits, solar energy also delivers:
- More stable energy prices because the sun is predictable and “renewable” (in this case, meaning that it does not get used up). Fossil fuel prices fluctuate with supply and demand.
- Long-term availability since the sun is here for the long term (assuming we don’t obscure its rays with greenhouse gases). Fossil fuels are finite resources. They will run out. The search for new fossil fuels is what led to fracking.
- New jobs in areas including research, manufacturing and installation to offset declining jobs in the fossil fuel industry.
There you have it: Oodles of proof that installing solar energy for your home or business not only saves you money; it delivers proven, quantifiable environmental and human health benefits, all of which make this planet a better place to live, and may improve the health of you and your family.



